Connect to Docker Container on a Remote Server over SSH
Contents
- The problem
- Mounting a Docker container
- Mounting a Docker Container with SSH enabled
- Connect via command line
- Connect via VSCode
The problem
I work a lot with Machine Learning and Deep Learning algorithms wrote in Python. Because of the various framework available (such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, RAPIDS, TPOT …) I use Docker a lot, usually along with a Jupyter-enabled image (see my other article if you are interested) which allows me to do all the prototyping I need in a fast and clean way. It is common to put such containers on a remote server with the required hardware (mostly GPUs) rather than developing on the local machine.
Sometimes, though, JupyterLab is not enough, and some good old VSCode coding is the best thing I can hope for, especially when dealing with Python packages development which I will then have to test with Jupyter. And here we encounter our problem:
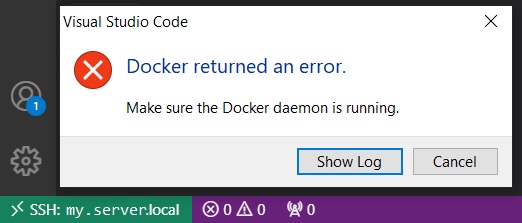
VSCode does not allow to connect to a remote container on a remote server. In fact, it just allows you to connect to a remote machine or to your local containers. If we attach VSCode to our remote server:
and then we try to attach VSCode to a running container on the remote server:
we get the following error:
The best solution, in this case, is to enable SSH tunneling directly from the Docker container, allowing VSCode to seamlessly connect to the container as if it was a standalone remote machine:
Mounting a Docker container
Let’s use the Jupyter-enabled image we mentioned before as the base image for our container. After pulling it from dockerhub:
docker pull davidelanz/jupyter
we can mount it exposing the container’s Jupyter port 8888 on, for example, my.server.local:2345 using the option --publish <SERVER-PORT>:<CONTAINER_PORT> (or -p), which publish a container’s port (8888) to the server’s specified one (2345):
docker run\
-p 2345:8888 \
--name my-jupyter-workspace \
davidelanz/jupyter
Now we can access Jupyter at my.server.local:2345, but can’t attach VSCode nor connect via SSH to my-jupyter-workspace container.
Mounting a Docker Container with SSH enabled
In order to enable the SSH tunnel, we first have to expose the container’s SSH port 22 to a server port. In our case, we will use my.server.local:2344:
docker run\
-p 2344:22 \
-p 2345:8888 \
--name my-jupyter-workspace \
davidelanz/jupyter
Now, we have to enter the container. First, we enter the server via SSH:
ssh my.server.local
Then, we attach to the container with:
docker container exec -it my-jupyter-workspace /bin/bash
Now we are finally inside our running container, and we can install a SSH server directly in it:
apt-get update && \
apt-get upgrade -y && \
apt-get -y install openssh-server && \
mkdir -p /var/run/sshd && \
service ssh start
If it was not already set, we have to change then the root’s password in order to log in during SSH authentication process:
echo "root:<NEW_PASSWORD>"|chpasswd
Now we are able to start the SSH server process via service ssh restart, but we
still can’t log in. In fact, we have to authorize SSH connection with a root account.
In order to do that, we need to go to /etc/ssh/sshd_config and modify the option
PermitRootLogin from prohibit-password to yes.
Moreover, if it is not commented, comment the UsePam yes line.
We can open the text file with GNU nano:
apt-get install nano && nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
| Before | After | |
|---|---|---|
# PermitRootLogin prohibit-password |
→ | PermitRootLogin yes |
UsePAM yes |
→ | #UsePAM yes |
Then we just need to restart our ssh process:
service ssh restart
Connect via command line
Now we can connect via command line at ports 2344 of docker server using the
address of the remote server (my.address.local)
specifying the port in SSJ with -p <port>:
ssh -p 2344 my.address.local
Connect via VSCode
We can now add my.address.local:2344 to the SSH configuration file:
Host my-remote-container
HostName my.address.local
User root
Port 2344
ForwardAgent yes
and we can use the VSCode Remote Explorer tool to attach VSCode directly to the container running on the remote server.